Accessing the nmpost cluster with VNC
Accessing the nmpost cluster with VNC
While ssh will work fine if you are on the internal NRAO network, if you are trying to display things from a remote site we recommend using VNC.
Connect to the NRAO
If you are NRAO staff, from your local machine, log in to the ssh portal login.aoc.nrao.edu with your username (e.g., gmarx). Skip this section if you are physically at the NRAO.
If you are not NRAO staff, from your local machine, log in to the ssh portal guest-login.aoc.nrao.edu with your username (e.g., nm-4386). Skip this section if you are physically at the NRAO.
Please note that the screenshots below reference the host "ssh.aoc.nrao.edu". If you are a non-staff member, you will need to substitute the host "guest-login.aoc.nrao.edu".
For Linux and Mac machines
ssh nm-4386@ssh.aoc.nrao.edu
For Windows machines
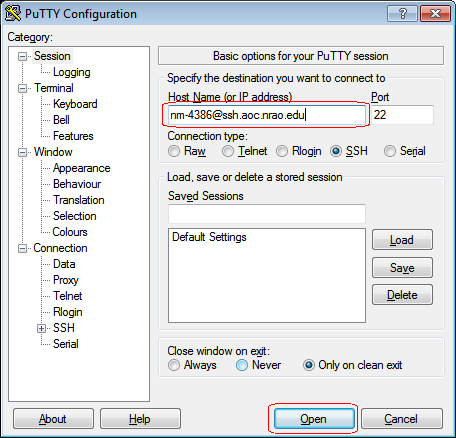
Install PuTTY, fill in the Host Name field and click Open.
Start the VNC server
From the ssh portal, or some other NRAO machine, login to the node assigned to you (e.g. nmpost050)
ssh nmpost050
and start a VNC server with the following command
vncserver
The first time you run this, it should prompt you to set a password. Do not use the same password as your username. The system should then return something like:
New 'nmpost050:1 (nm-4386)' desktop is nmpost050:1
The 1 in this example is your session. You will need this number later when you use your VNC client.
Connect to the VNC server
The VNC Client used to connect to the VNC server is different depending on the OS you are using (Linux/RHEL, Linux/Ubuntu, MacOS)
Linux (RHEL, CentOS, SL, OEL, Debian)
If your local machine is an RHEL or Debian derivative, use vncviewer to start the VNC connection like so (assuming the session number is 1)
vncviewer -via nm-4386@ssh.aoc.nrao.edu nmpost050:1
If you are physically at the NRAO, skip the "-via" syntax like so
vncviewer nmpost050:1
Linux (Ubuntu)
If your local machine is Linux/Ubuntu, use remmina to start the VNC connection like so (assuming the session number is 1)
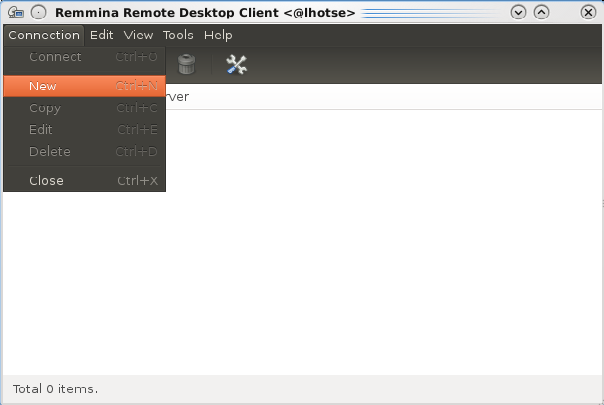
Launch the remmina program and select Connection -> New
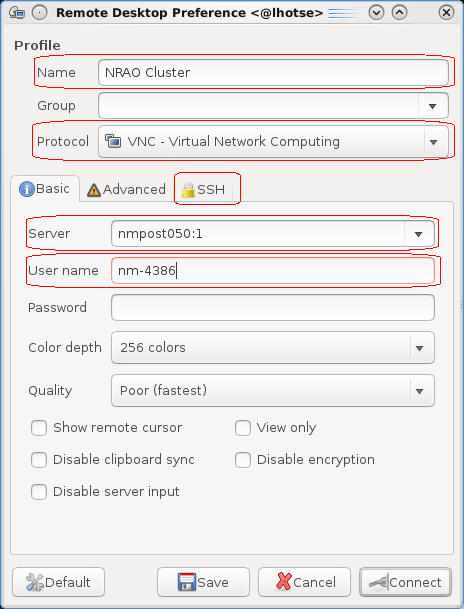
Set the Name to something descriptive like NRAO Cluster, change the Protocol to VNC - Virtual Network Computing, set the Server to the node assigned to you followed by a colon and the session number (e.g. nmpost050:1), set the User name (e.g. nm-4386). Then select the SSH tab
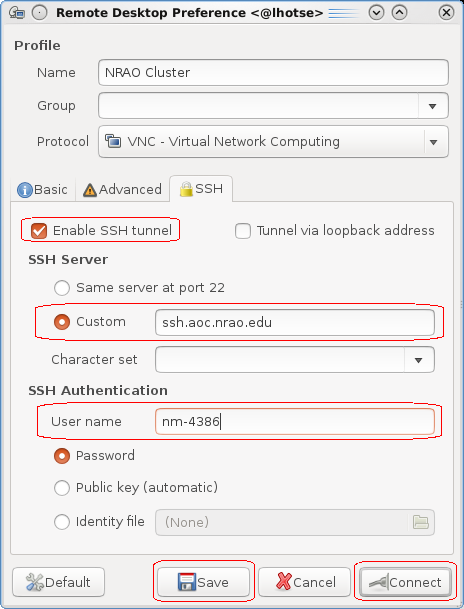
Check the box for Enable SSH tunnel, select Custom and set it to ssh.aoc.nrao.edu, set the User name (e.g. nm-4386), click on Save. The window will disappear (Ubuntu 16+) so then right-click on the entry for this connection in the main remmina window and then choose and then Connect.
Mac
Open the Applications folder then the Utilites folder then double-click on the Terminal application. In the terminal, start an SSH tunnel like below. In the following examples, 590Y is derived by adding 5900 to the session number from above. Skip this step if you are on the NRAO internal network (Note: if you are connecting from the guest WiFi, you cannot skip this step!). For the local Mac, choose a number for X that is not 1 (5901 cannot be used and will result in error if used) represented by the 590X below. Replace X in the example with that chosen number (e.g., 5902, 5903, etc.).
ssh -L 590X:nmpost050:590Y nm-4386@ssh.aoc.nrao.edu
Leave that terminal in the background. Then in the Finder, Pull down the GO menu and choose Connect to Server. For the server address, specify:
vnc://localhost:590X
You will be challenged for the VNC password you set up (likely at the time you launched the vnc server).
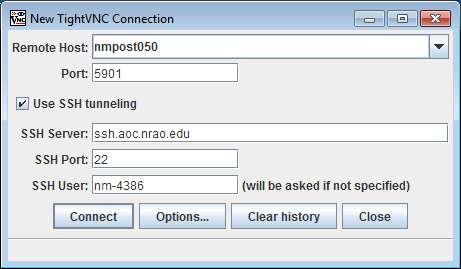
Windows
Use a VNC client like the Java Viewer from TightVNC with the following setup. The port number can be found by adding 5900 to the session number. So in the above example, with a session number of 1, the port will be 5901. If you are physically at the NRAO, leave the "SSH Server" line blank.
End the VNC server
Commands that are run in this VNC session will continue to run even after closing your local VNC client. Once all processes are done, you should close your VNC server by connecting via ssh again to the cluster node and running the following (assuming the session number is 1)
vncserver -kill :1
Common difficulties
RHEL8 issues
Issues may arise from the upgrade to RHEL8. Many of these can be solved by exiting VNC and making sure it is no longer running (e.g. vncserver -kill :1), removing your xstartup (e.g. rm -f ~/.vnc/xstartup), and restarting VNC (e.g. vncserver).
Black screen on RHEL8
Since the upgrade to RHEL8, it has become more common for users to encounter a black screen when attempting to connect to a VNC session. This usually happens when more than one VNC server session is started. The default xstartup file provided with RHEL 8 does not work well. As a workaround, run the following and then restart VNC.
echo '#!/bin/sh' > ~/.vnc/xstartup
echo 'dbus-launch --exit-with-session gnome-session' >> ~/.vnc/xstartup
chmod 755 ~/.vnc/xstartup
Terminal window fails to open
If you find you are unable to open gnome-terminal or xterm in the VNC session and you are using a MacOS machine, try the following.
This happens often for MacOS users. Navigate to your teminal app's settings and then to the profiles. Somewhere (the location changes per MacOS version) there should be a checkbox to "Set local variables automatically". Uncheck this, restart the terminal on your MacOS machine, kill the prevous VNC server on the NRAO machine and try the process again.
What is happening is the MacOS machine is setting the LC_CTYPE environment variable which is getting propagated via ssh to the NRAO machine and into the VNC server where many programs like gnome-terminal, xterm, etc read this and can be confused by it.

