National Radio Quiet Zone (NRQZ)
The National Radio Quiet Zone (NRQZ) was set aside by the federal government to provide a geographical region to protect sensitive instrumentation from Radio Frequency Interference (RFI).
Description
The NRQZ was established by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in Docket No. 11745 (November 19, 1958) and by the Interdepartment Radio Advisory Committee (IRAC) in Document 3867/2 (March 26, 1958) to minimize possible harmful interference to the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) in Green Bank, WV and the radio receiving facilities for the United States Navy in Sugar Grove, WV. The NRQZ is bounded by NAD-83 meridians of longitude at 78d 29m 59.0s W and 80d 29m 59.2s W and latitudes of 37d 30m 0.4s N and 39d 15m 0.4s N, and encloses a land area of approximately 13,000 square miles near the state border between Virginia and West Virginia.
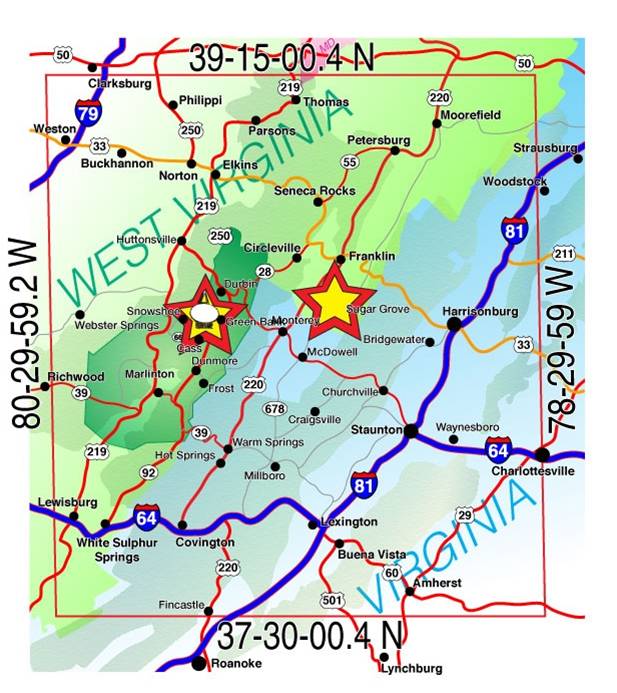
The National Radio Quiet Zone (NRQZ) contains the Green Bank Observatory, and the Sugar Grove site.
Coordination Requirements
NRQZ coordination is required for all new or modified, permanent, fixed, licensed transmitters inside the NRQZ, as specified for federal transmitters by NTIA manual section 8.3.9 and for non-federal transmitters by the FCC in 47 CFR section 1.924.
Coordination under the West Virginia State Code Chapter 37A “Radio Astronomy Zoning Act” (WVRAZ) may also apply.
Voluntary Coordination with the NRQZ office is greatly appreciated for frequency assignments that are not required to coordinate.
Coordination Process
Background: In order to minimize harmful interference to the operations in Green Bank and the Sugar Grove Research Station, all requests for new or modified, permanent, fixed, assigned or licensed transmitters within the NRQZ shall be coordinated by the applicant, prior to submission to the FCC or NTIA.
We emphasize that the Interference Office has no authority in the granting of an FCC license or a Federal Government frequency assignment. The Interference Office only has the privilege of submitting its comments on a particular transmitter installation to the FCC or IRAC.
Requirements: Download and fill out the NRAO AutoPath Applicant Submission Template excel worksheet to the best of your ability. Please take special note to the format and units of the required fields. A single excel worksheet can be used for multiple locations, frequencies, transmitter, etc. The NRQZ Office also requires the applicants mailing address, and may require antenna patterns where applicable. Email your completed excel worksheets, mailing address, and antenna patterns to the NRQZ Program Administrator at nrqz@nrao.edu.
The NRQZ Program Administrator will pass the application to the Sugar Grove Research Station for their analysis. Please do not reach out to the Sugar Grove Research Station.
Analysis: The NRQZ office reviews all applications to ensure that the computed power flux density at the reference point does not exceed frequency-dependent thresholds. The NRQZ Office initially analyzes each application as a worst-case scenario. If this worst-case scenario fails, the applicant will be required to fill out a site inspection worksheet to demonstrate the design will not cause RFI to the Green Bank Observatory. Please note, this worst-case scenario often does not include antenna patterns. If you have any further questions about the analysis, reach out to the NRQZ Program Administrator at nrqz@nrao.edu.
If your proposed system meets the NRAO protection criteria, you will receive a coordination letter suitable to attach to an FCC application or NTIA assignment. The NRQZ office does not concur with any applications until a coordination letter has been issued.
Calculation Tools
Power Density Thresholds
Based on a 20 kHz measurement bandwidth, the calculated power density of the transmitter at the reference point should be less than:
1 x 10-8 W/m2 for frequencies below 54 MHz
1 x 10-12 W/m2 for frequencies from 54 MHz to 108 MHz
1 x 10-14 W/m2 for frequencies from 108 MHz to 470 MHz
1 x 10-17 W/m2 for frequencies from 470 MHz to 1000 MHz
freq2 (in GHz) x 10-17 W/m2 for frequencies above 1000 MHz
With the exception frequencies that reside in the radio astronomy observing bands listed in the US Table of Frequency Allocations, in which case the power densities listed in Table 1 of Recommendation ITU-R RA.769 shall apply. For a comprehensive list, click here.
Reference Point
The reference point for calculations of transmitter power density is the prime focus of the Green Bank Telescope (GBT). The location of the GBT prime focus is:
Latitude: 38d 25m 59.2s N (NAD83)
Longitude: 79d 50m 23.4s W (NAD83)
Ground Elevation: 806 Meters or 2644 Feet AMSL (NAVD88)
Height: 139.6 Meters or 458 Feet AGL

